Coral-García Miguel Ángel, Serrano-Guevara Christian Mauricio, León-López Magdalena, López-Santos Héctor Alfonso, Barbosa-Contreras Meylin, Maldonado-Castañeda Sandra, Rubio-Nava Karla María, Guevara-Navarrete César Martín, Silva-Campos Irlanda Mariel and Yaneth Martínez Tovilla*
Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Pediatric Patient
Abstract
Introduction:Aspergillusis a branched septate filamentous fungus that can induce lethal and invasive infections in patients suffering from autoimmune or inflammatory diseases, as well as patients undergoing organ transplantation and/or treatment for malignantneoplasms [5].
Since aspergillosis is not a reportable infection in many countries, it is difficult to have an accurate estimate of thenumber of cases worldwide. Even so, most cases of this disease are sporadic and occasionally in hospitalized patients, with a reported mortality of 30% to 85% [6]
Voriconazole is the recommended drug in invasive aspergillosis, which is an azole agent that inhibits cytochrome P450 (CYP450)-dependent demethylation of 14α-lanosterol in the synthesis of ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane [7].
The importance of this work lies in the need to recognize in early stages this pathology, often diagnosed in autopsies. Therefore,we offer a clinical perspective on the comprehensive approach to invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in a pediatric patient.
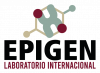
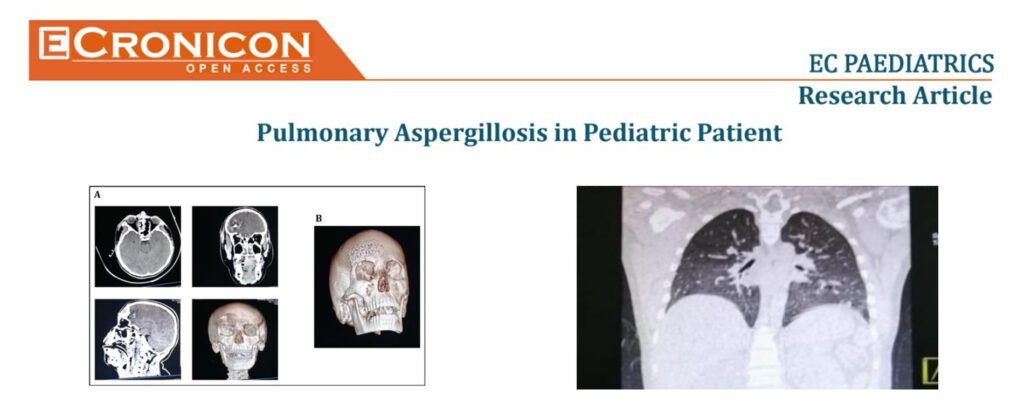
Case:15-year-old male with no relevant history. He was admitted to the General Hospital of Puebla “Dr. Eduardo Vazquez Navarro” after suffering trauma to the frontal bone of the skull (kicked by an equine). After his recovery, he presented fever despite administra-tion of ceftriaxone and vancomycin, for which reason meropenem was added and a bronchial aspirate culture was obtained with a report ofAspergillus fumigatus; a positive determination of galactomannan in bronchial aspirate; a chest CT scan with ground glassimage in the right upper lobe, consolidation at the level of segments 6-10 right and right basal laminar atelectasis.
Overall, a diagnosis of pulmonary aspergillosis was made and treatment with voriconazole was started. Once stable, the patient was discharged withthe following drugs: voriconazole, levetiracetam, carbamazepine, captopril, omeprazole, beclomethasone and prednisone, as well asfollow-up and outpatient appointment by the pediatrics, neurology, pneumology and cardiology specialties.
Pulmonary aspergillosis is a disease that induces high mortality due to its late diagnosis. Early diagnosis and efficient targeted therapy had a positive impact on the prognosis of this patient.Aspergillusinfections can be catastrophic in different situations. Clinical suspicion and efficient use of different healthcare resources (e.g. laboratory and imaging studies) can improve the prognosis ofthese patients.